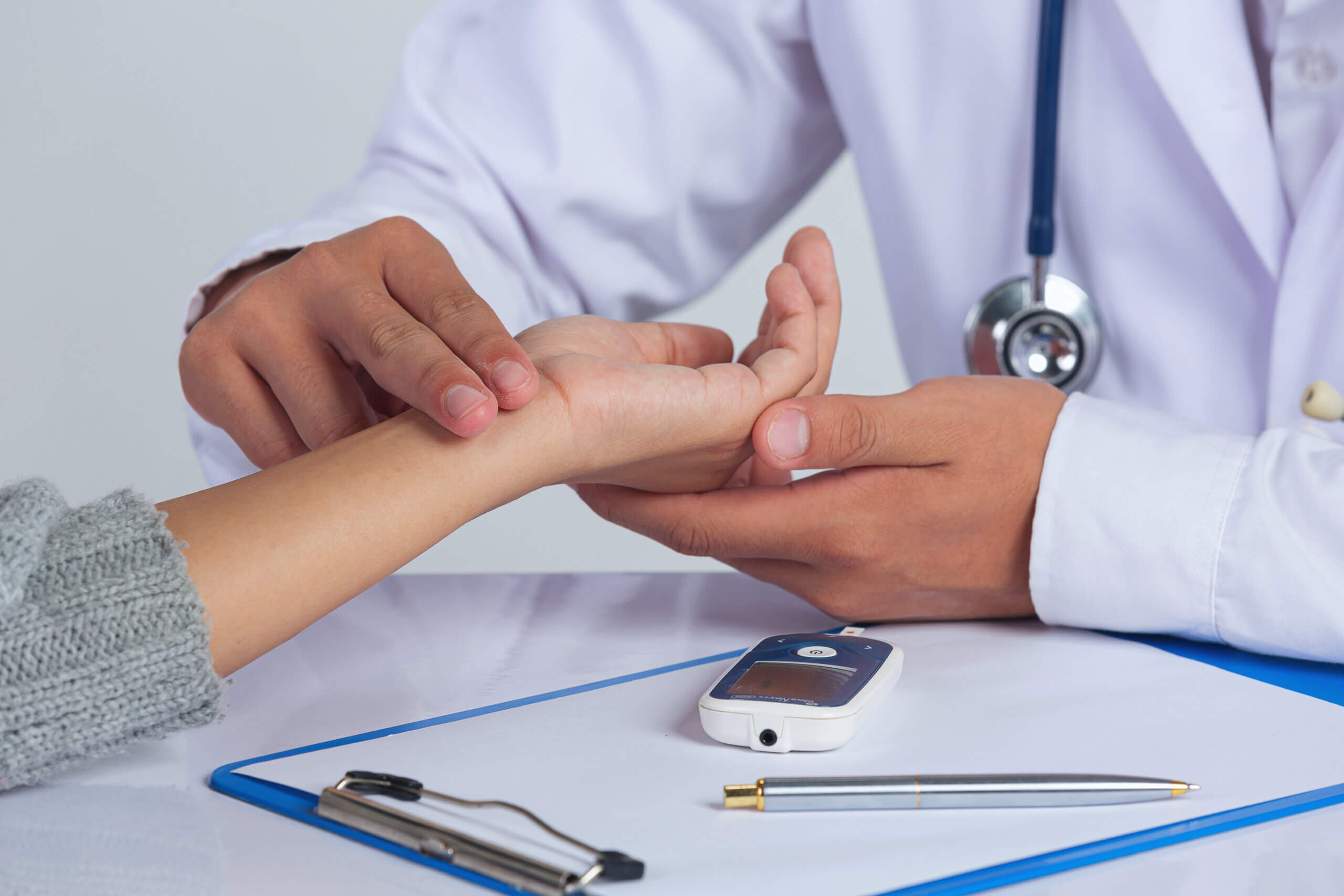
Are you one of those individuals who ponder on the complexity of health, always seeking to understand the why and how? You’re not alone. For health-conscious minds, the quest to unravel the mysteries of the human body is unending. And today, you will learn about a health topic that touches millions of lives worldwide — diabetes.
Let’s begin with the basics. What exactly is diabetes?
It’s not just a condition; it’s a global health phenomenon. Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. The impact of diabetes resonates across the globe, affecting millions and posing significant challenges to healthcare systems and individual well-being.
The significance of diabetes cannot be overstated. It’s a condition that’s both pervasive and personal, touching lives in every corner of the world. Diabetes knows no boundaries – age, gender, or geographic location. The statistics are staggering. Over 400 million people worldwide have diabetes, and this number is growing at an alarming rate.
This condition affects not only individuals but also their families, communities, and societies at large. The implications are far-reaching – from the burden on healthcare systems to the personal struggles faced by those living with diabetes.
In this blog post, you will be equipped with a comprehensive understanding of diabetes. You’ll learn about the intricacies of this condition, exploring its types, causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and management. Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your health and the health of your loved ones. Whether you’re seeking to prevent diabetes, manage it effectively, or support someone on this path, this guide will be your trusted resource.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is not a one-size-fits-all condition. It’s a complex interplay of factors that give rise to different types of diabetes. Understanding the types of diabetes there is is key to grasping the condition as a whole.
Type 1 Diabetes: Unmasking the Immune Attack
Type 1 diabetes is often described as an autoimmune condition. In this case, the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The precise cause remains a puzzle, but it’s believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Type 1 diabetes typically manifest abruptly. They include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and irritability. Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to a condition called ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency.
Management
Management of Type 1 diabetes revolves around the replacement of insulin, the hormone the body can no longer produce. Patients are often prescribed insulin injections or insulin pumps to control blood sugar levels. Close monitoring of blood sugar, along with a balance of diet and physical activity, is crucial for effective management.
Type 2 Diabetes: Unmasking Lifestyle Factors
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors. It can be triggered by obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary choices. Genetics also play a role, and some individuals may be more predisposed to developing this type.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes can develop more gradually. These may include increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow wound healing. Some individuals with Type 2 diabetes may not display noticeable symptoms at first.
Management
Managing Type 2 diabetes often begins with lifestyle changes. This includes adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and losing weight if necessary. Medications and, in some cases, insulin therapy may also be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring and routine check-ups are vital components of managing Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes: A Temporary Challenge for Moms-to-Be
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs only during pregnancy. It develops when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet increased needs during pregnancy. The exact causes are not entirely clear, but hormonal changes and genetic factors are believed to play a role.
Risks During Pregnancy
Developing gestational diabetes can present risks for both the mother and the baby. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels may increase the risk of high birth weight in the baby, which can lead to complications during delivery. It can also raise the risk of preterm birth and low blood sugar in the baby after birth.
Management
The management of gestational diabetes focuses on maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range to minimize risks. This is often achieved through a combination of dietary modifications and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. Some women may require insulin injections if lifestyle changes are not sufficient. Managing gestational diabetes is critical to ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a good start for both mother and baby.
Understanding Insulin: The Body’s Blood Sugar Regulator
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas with a key role in regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels.
Role of Insulin in the Body
When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. High blood sugar levels can be harmful, so insulin acts as a messenger, allowing glucose to enter your body’s cells. Once inside the cells, glucose is either used for energy or stored for later use. This process helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, ensuring your cells receive the energy they need to function properly.
How Insulin Resistance Develops
Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, the pancreas tries to compensate by producing more insulin, resulting in higher insulin levels in the bloodstream. This state can lead to various health problems, including type 2 diabetes. The exact causes of insulin resistance are not fully understood but may include genetic factors, obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats.
Risk Factors for Diabetes: Unveiling the Culprits
Genetic Factors
Diabetes often has a strong genetic component. If you have close family members with diabetes, especially parents or siblings, your risk increases. This doesn’t mean you’ll definitely get diabetes, but it’s a factor to be aware of.
Lifestyle Factors
Your daily habits play a crucial role. Sedentary lifestyles, lack of exercise, and poor dietary choices can significantly elevate your risk. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management are key in mitigating these lifestyle-related risks.
Obesity and Its Connection to Diabetes
Obesity is one of the most significant contributors to type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance. The fat cells themselves can release chemicals that interfere with insulin’s action. Addressing obesity through lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, can substantially lower your risk.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Frequent Urination: You find yourself making more trips to the bathroom, especially at night.
Excessive Thirst: Increased urination often leads to feeling excessively thirsty.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating as usual or more, you’re losing weight.
Fatigue: You experience persistent tiredness and a lack of energy.
Blurry Vision: Diabetes can affect your eyes, leading to blurred vision.
Slow Wound Healing: Cuts and bruises take longer to heal.
Tingling or Numbness: You might experience tingling or numbness in your hands or feet.
Recurrent Infections: Diabetes can weaken your immune system, leading to frequent infections.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and enable effective management. Diabetes left untreated or uncontrolled can lead to heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and more. If you notice these signs, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. An early diagnosis can make a world of difference in effectively managing diabetes.
Diagnosis and Testing: Key Steps in Confirming Diabetes
Blood Sugar Tests
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
This test measures your blood sugar level after an overnight fast. If your fasting blood sugar is higher than 126 mg/dL on two separate tests, it may indicate diabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
In this test, your blood sugar is measured after fasting, then you consume a sugary solution, and your blood sugar is tested again after two hours. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher two hours after the sugary drink suggests diabetes.
Hemoglobin A1c Test
This test reflects your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
Note: These tests should be interpreted by a healthcare professional to confirm the diagnosis.
Complications of Diabetes: Managing the Long and Short Term
Short-term Complications
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
This occurs when blood sugar drops too low. Symptoms may include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and even fainting. It’s important to treat hypoglycemia immediately by consuming glucose or a sugary snack.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
This is the opposite of hypoglycemia. When blood sugar levels remain high, it can lead to symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Hyperglycemia requires careful management of your diabetes medications.
Long-term Complications
Cardiovascular Issues
Diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Regular check-ups and a heart-healthy lifestyle can help manage these risks.
Neuropathy
This condition affects the nerves and can lead to numbness, pain, or even ulceration in the feet. Proper foot care and blood sugar control are key.
Kidney Disease
Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney problems. Managing blood sugar levels and blood pressure, along with routine kidney check-ups, is crucial.
Eye Problems
Conditions like diabetic retinopathy can affect vision. Regular eye exams are necessary for early detection and intervention.
Diet and Nutrition: Fueling a Healthy Life with Diabetes
Role of Diet in Diabetes Management
The right diet plays a central role in managing diabetes. By understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels, you can make healthier choices. Your diet should be a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to keep your blood sugar stable.
Best Foods for Diabetics
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are rich in nutrients and low in carbohydrates.
Whole Grains: Oats, quinoa, and brown rice provide fiber, which slows the absorption of sugar.
Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes are excellent sources of protein without excessive fat.
Healthy Fats: Avocado, nuts, and olive oil are sources of good fats.
Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and other berries are low in sugar and high in antioxidants.
Importance of Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) ranks carbohydrates in foods on a scale of 0 to 100 based on how they affect blood sugar levels. Low-GI foods release glucose slowly and steadily, providing a steady supply of energy, which is ideal for people with diabetes.
Understanding the GI of foods helps diabetics make choices that keep their blood sugar in check. A diet rich in low-GI foods can help with blood sugar control and overall health.
Exercise and Physical Activity: Empowering Diabetics
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing diabetes. Here are some of its key benefits:
Blood Sugar Control: Physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively, reducing blood sugar levels.
Weight Management: Exercise contributes to weight loss and maintenance, which is crucial for Type 2 diabetics.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Regular physical activity can make your cells more responsive to insulin.
Reduced Heart Disease Risk: Exercise supports cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Stress Reduction: Physical activity helps lower stress levels, which can impact blood sugar control.
Types of Exercises Suitable for Diabetics
Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling improve heart and lung health while helping control blood sugar.
Strength Training: Building muscle enhances insulin sensitivity, so consider weightlifting or resistance exercises.
Flexibility Exercises: Stretching can improve flexibility and balance, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
Yoga: This combines flexibility, strength, and stress reduction, making it an excellent choice for diabetics.
Note: Remember to consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise program, especially if you have underlying health issues.
Medications and Insulin Therapy: Balancing Blood Sugar
Oral Medications
For many people with Type 2 diabetes, oral medications are prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. These drugs work in various ways, such as:
Stimulating Insulin Production: Some drugs prompt the pancreas to release more insulin.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity: Others enhance the body’s response to insulin.
Reducing Sugar Production: Certain medications lower the liver’s glucose production.
Delaying Carb Absorption: Some drugs slow the absorption of carbohydrates in the digestive system.
Insulin Therapy
People with Type 1 diabetes and some with Type 2 may require insulin therapy. Insulin can’t be taken orally; it must be injected or administered via an insulin pump. Types of insulin include:
Rapid-Acting Insulin: Works quickly and is taken before meals to control post-meal blood sugar spikes.
Short-Acting Insulin: Begins working within 30 minutes and lasts 3-6 hours.
Intermediate-Acting Insulin: Onset is slower, but it lasts longer, often covering blood sugar levels for half a day.
Long-Acting Insulin: Provides a steady release of insulin over an extended period, typically a full day.
New Advancements in Diabetes Treatments
Research into diabetes treatment is ongoing. Some exciting advancements include:
Artificial Pancreas: These devices continuously monitor blood sugar levels and administer insulin as needed.
Insulin Patches: Instead of injections, patches are being developed for more convenient insulin delivery.
Inhaled Insulin: An alternative to injections or pumps, inhaled insulin is becoming more widely available.
Stem Cell Therapy: Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to replace damaged pancreatic cells in Type 1 diabetics.
Closed-Loop Systems: Combining continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pumps for better blood sugar control.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes: Shifting the Odds in Your Favor
Strategies to Reduce Diabetes Risk
While you can’t change your genetics, several lifestyle choices can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes:
Healthy Diet: Adopt a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize sugar, processed foods, and excessive carbohydrates.
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Shedding even a few pounds can make a big difference.
Blood Pressure Control: Manage your blood pressure through a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and, if needed, medication.
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Seek support to quit this habit.
Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol can lead to blood sugar imbalances. Consume it in moderation.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels. Incorporate relaxation techniques into your routine.
Healthy Living Choices
Maintaining a diabetes-friendly lifestyle means making choices that positively impact your health:
Balanced Meals: Create balanced meals with a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Monitor portion sizes.
Regular Monitoring: If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication, adhere to your treatment plan and take medicines as directed.
Consistent Exercise: Keep up with regular physical activity to help manage blood sugar levels.
Stress Reduction: Explore stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your diabetes and overall health.
Healthy Recipes for Managing Blood Sugar
Below are some foods that help you manage your blood sugar.
Okra Soup: This Nigerian staple is rich in fiber and low in carbs. Prepare it with a lean source of protein, like grilled chicken or fish, and pair it with a high-fiber grain like brown rice or whole wheat fufu.
Garden Egg Sauce: This dish is packed with fiber and nutrients. Make it with tomatoes, onions, and lean ground turkey. Serve it with a side of quinoa for a balanced meal.
Moi Moi: This steamed bean pudding is an excellent protein source and low in carbohydrates. You can make it with minimal oil and enjoy it with a side of fresh vegetables.
Bitter Leaf Soup: Bitter leaf is known for its blood sugar-lowering properties. Cook it with fish or lean beef and serve with whole-grain eba for a fiber-rich meal.
Taking Charge of Your Health
In the journey of understanding diabetes and its many facets, you’ve uncovered the keys to managing this condition.
Remember, a health-conscious lifestyle is your most potent weapon against diabetes. Making informed choices, staying active, and embracing diabetes-friendly meals will help you navigate this journey with confidence. As you continue your quest for health and wellness, know that understanding and managing diabetes is a testament to your commitment to a vibrant, fulfilling life. Here’s to a healthier, happier you!
Additional Resources for Your Diabetes Journey
Your quest to understand and manage diabetes doesn’t have to end here. There’s a wealth of information and support available to help you on your journey to a healthier, more vibrant life. Below are some book recommendations to provide you with valuable insights and assistance:
Books
1. “Diabetes for Dummies” by Alan L. Rubin, MD – A comprehensive guide that breaks down the complexities of diabetes in an accessible way.
2. “The End of Diabetes: The Eat to Live Plan to Prevent and Reverse Diabetes” by Dr. Joel Fuhrman – Learn how to transform your diet and take control of your health.
At Metro Health HMO, we are dedicated to promoting health and well-being. We provide you a range of healthcare services, including diabetes management programs. Visit our website for more information on how we can support you on your journey.
Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. Metro Health HMO is always here to help you live your best, healthiest life.